Contents
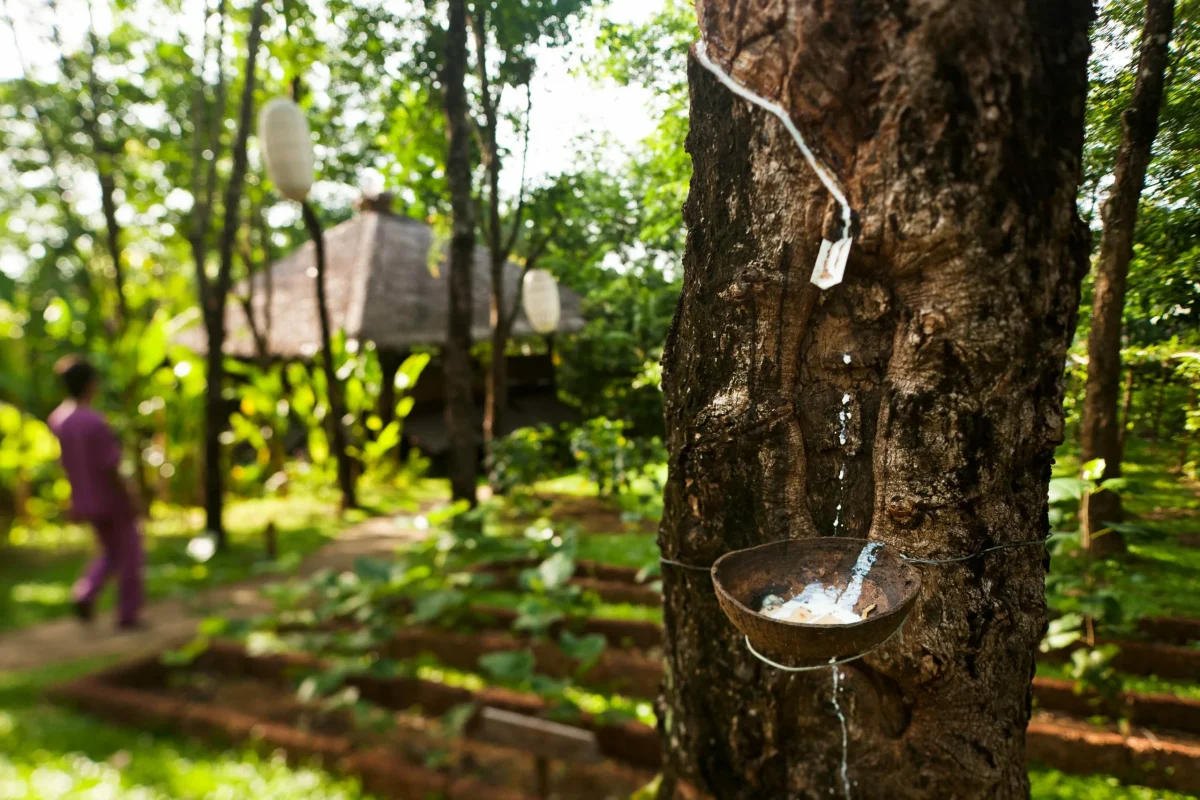
Natural rubber latex is the essential latex material behind a wide range of medical, industrial, and consumer latex rubber products. Its elasticity, purity, and stability play a decisive role in how well these products perform during use and how efficiently they can be processed in manufacturing.
At Ngoc Chau Natural Rubber, we place strong emphasis on controlling latex quality from the very first stage, ensuring that every batch meets the stringent technical parameters required for modern rubber processing and high-performance latex rubber products applications.
Why Rubber Content & Stability Parameters Matter in Latex Rubber Products
The performance of a latex solution depends not only on its origin but also on its intrinsic physicochemical characteristics. Two foundational aspects define whether a latex is suitable for production: rubber content (the percentage of dry rubber) and the overall stability of the rubber solution during processing. To evaluate these properties effectively, the global rubber industry relies on three critical quality parameters: DRC (Dry Rubber Content), MST (Mechanical Stability Time) and VFA (Volatile Fatty Acids) — all of which define the consistency and quality of latex rubber products.
- DRC indicates the actual amount of dry rubber in the latex, influencing film formation, viscosity, and yield efficiency.
- MST reflects the latex’s resistance to mechanical stress without coagulating — a key requirement for dipping applications.
- VFA measures the freshness and chemical stability of latex, determining its storage life and resistance to degradation.
When these parameters are properly controlled, the latex becomes a high-performance rubber solution — stable, uniform, and optimized for manufacturing gloves, rubber thread, foam latex, adhesives, and various industrial components. This quality framework is also the foundation that Ngoc Chau consistently upholds across our production and supply processes.
Dry Rubber Content (DRC)
What is DRC in rubber?
Dry Rubber Content (DRC) — the full form of DRC in rubber — is the mass of dry rubber in 100 grams of latex, used to determine the quality, concentration, and value of natural rubber latex. It shows how much actual dry rubber remains after water is removed, making it the key indicator of latex purity and commercial worth.
DRC is often referred to as percent latex because pricing depends directly on the solid rubber content. In industry, dry rubber content in latex is a critical parameter for evaluating DRC material, controlling chemical dosing, and ensuring stable processing performance.
Method of Determination
DRC is typically measured using the oven-drying method. A latex sample is dried until only the solid rubber remains, and this mass is weighed to calculate the dry rubber content in latex. Modern factories also use electronic or microwave DRC meters for faster and more consistent measurements.
Applications in Industry
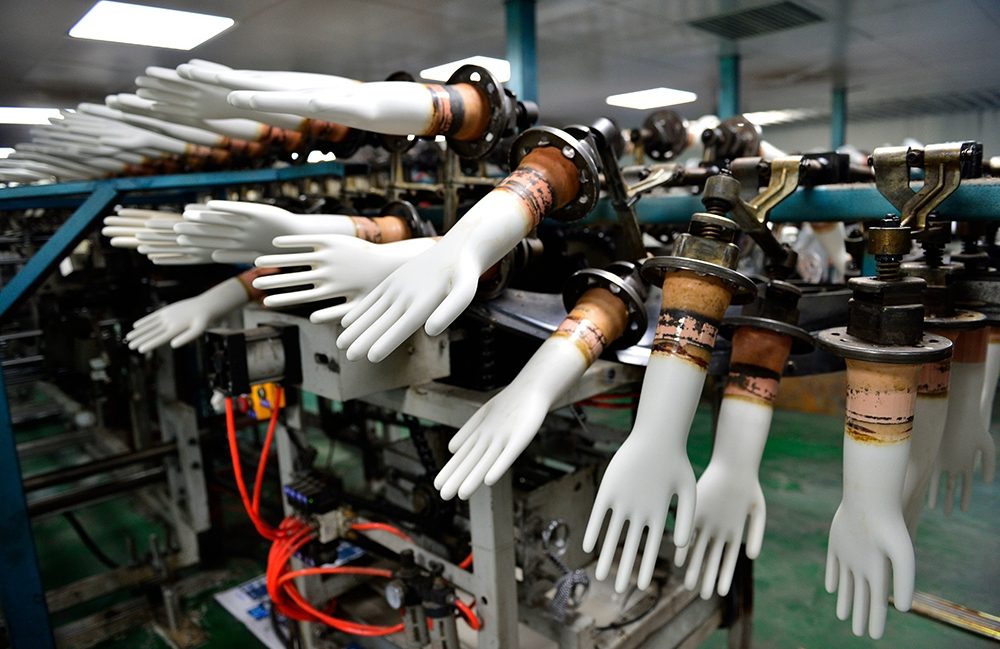
High-DRC latex is crucial for durable, high-stress latex rubber products, including:
- Gloves: supports strong, elastic medical and industrial gloves.
- Mattresses & foam: improves support, breathability, and lifespan.
- Automotive components: ideal for gaskets, seals, and vibration-absorbing parts.
Mechanical Stability Time (MST)
What is MST in rubber?
Mechanical Stability Time (MST) is a measure of a latex’s resistance to coagulation under mechanical stress, such as continuous stirring or high-shear mixing. A higher MST means the latex is more stable and less likely to clump, break down, or coagulate during processing.
This makes MST a critical quality parameter for manufacturers who need consistent latex behavior during dipping, compounding, and film-forming processes.
Method of Determination
MST is determined through a mechanical stress test, where latex is agitated at a constant speed using a standardized mechanical stirrer.
- Samples are periodically examined for the first visible signs of coagulation.
- The MST value is the time from the start of agitation until coagulum appears.
- Industry standards such as ISO 35 ensure accuracy and consistency in testing procedures.
A longer MST indicates better dispersion stability and improved resistance to shear forces.
Importance in Industry
High MST values are essential in applications where latex undergoes strong mechanical handling:
• Predictable Process Performance
Latex with high MST is less likely to coagulate during mixing, pumping, dipping, or centrifugation.
• Quality and Consistency
Stable MST reduces production downtime, prevents defects, and increases consistency in products such as gloves, balloons, foam, adhesives, and coatings.
• Procurement Standard
For many factories, MST is a procurement requirement when evaluating materials for latex rubber products.
Volatile Fatty Acid (VFA) Levels
What are VFAs in rubber?
Volatile Fatty Acids (VFAs) are volatile organic acids—such as acetic, formic, and propionic acid—formed when microorganisms break down carbohydrates in natural rubber latex.
The presence of VFAs indicates microbial deterioration, meaning the latex has begun to spoil.
A high VFA number is a critical warning sign because it reflects the degree of microbial activity and directly affects latex stability and odor.
According to ISO 2004:2010(E), the VFA number should not exceed 0.06 for concentrated latex used in latex rubber products.
How VFAs affect latex quality
VFAs have a strong impact on latex performance and processing:
• Indicator of spoilage
A high VFA number shows the latex is undergoing microbial degradation.
• Loss of colloidal stability
VFAs disrupt the protective colloid layer surrounding rubber particles, making the latex more susceptible to destabilization.
• Premature coagulation
Excess VFAs can trigger coagulation during storage, transport, or processing.
• Odor generation
High VFA levels can cause unpleasant smells during raw rubber drying.
• Impact on final product properties
Elevated VFA levels reduce the tensile strength and uniformity of the final rubber film.
Measuring VFA
The VFA number is the standard measurement for determining the amount of volatile fatty acids in latex.
It is assessed using analytical techniques described in international standards such as ISO 506:1992 and ISO 506:2020(en).
These standards define the procedures and tolerances for evaluating VFA levels in concentrated natural rubber latex, ensuring consistent quality control across the industry.
Additional Parameters to Consider
Although DRC, MST, and VFA are the core parameters for evaluating latex quality, several additional factors also play an important role in determining performance and processing behavior.
Besides DRC, MST, and VFA, other parameters influence the quality of latex rubber:
Total Solid Content (TSC)
Total Solid Content (TSC) represents the total percentage of all solids in latex—including dry rubber and non-rubber solids such as proteins, lipids, sugars, and minerals.
A higher TSC generally improves latex body, film-forming ability, and final product strength.
TSC is important for controlling viscosity, compounding formulations, and determining the efficiency of concentration processes.
Alkalinity / Ammonia Content
Alkalinity—commonly adjusted with ammonia (NH₃)—acts as a preservative to prevent microbial growth and premature coagulation.
Higher ammonia levels extend storage stability, but must be balanced to avoid excessive odor or incompatibility with specific product applications (e.g., low-ammonia latex for dipping).
Alkalinity is a critical factor in long-distance transport, shelf stability, and maintaining MST/VFA levels.
Viscosity
Viscosity indicates the flow behavior and thickness of latex.
It influences processing characteristics such as mixing, pumping, dipping, and especially applications like adhesives, coatings, and foam production.
Optimal viscosity ensures uniform spreading, proper penetration, smooth surface finishing, and predictable rheological behavior during manufacturing.
Applications of Latex Rubber Products
Natural rubber latex 60% DRC is a highly versatile latex material used across multiple industries. As one of the most reliable latex rubber products, it plays a critical role in manufacturing medical rubber products, industrial components, consumer goods, and specialty latex products. Its elasticity, stability, and film-forming ability make it suitable for a wide range of applications.
1. Medical Rubber Products (Gloves)
Latex 60% DRC is widely used in medical rubber products such as exam gloves, surgical gloves, and disposable gloves due to its high elasticity, comfort, and tear resistance.
2. Mattress & Pillow Manufacturing
Used in latex bed mattress, natural latex pillow, and latex foam products, offering superior breathability and long-lasting comfort.
3. Automotive Rubber Components
Ideal for shock absorbers, gaskets, seals, and other automotive latex products requiring flexibility and vibration resistance.
4. Adhesives & Coatings
A stable latex material used to produce rubber latex adhesive, liquid latex glue, and coatings for wood, paper, and textile applications.
5. Consumer & Specialty Latex Products
Commonly used in latex rubber balloons, natural latex condoms, and other specialty items where softness, elasticity, and safety are essential.
Conclusion
Understanding and controlling key latex parameters—including DRC, MST, VFA, and supporting factors like TSC, alkalinity, and viscosity—is essential for producing stable, high-quality latex rubber products in medical, industrial, and consumer rubber products. These indicators form the technical foundation that manufacturers rely on to maintain production efficiency, product durability, and process stability.
At Ngoc Chau Natural Rubber, we apply this quality framework across every batch we produce. If your business requires stable, high-performance latex rubber products for gloves, mattresses, adhesives, or industrial components, our technical team is ready to support you with reliable supply, consistent specifications, and tailored solutions for your production needs.
FAQs
1. What is DRC in natural rubber latex?
DRC (Dry Rubber Content) is the amount of dry rubber in 100 grams of latex. It determines latex purity, pricing, and how much usable rubber manufacturers can extract for production.
2. Why is MST important in latex processing?
MST (Mechanical Stability Time) shows how well latex resists coagulation under mechanical stress. High MST ensures smooth dipping, pumping, and mixing without clumping or defects.
3. What does a high VFA number indicate in latex?
A high VFA value signals microbial spoilage. It reduces latex stability, increases odor, and raises the risk of premature coagulation during storage or transport.
4. Which industries use natural rubber latex 60% DRC?
Latex 60% DRC is used in medical gloves, mattresses, foam products, adhesives, automotive parts, balloons, and condoms due to its strength, elasticity, and stability.
5. What parameters determine latex quality?
Latex quality is defined by DRC, MST, and VFA—supported by TSC, viscosity, and alkalinity. These parameters ensure consistent performance, stable processing, and high-quality end products.










 Ms Evan
Ms Evan