NATURAL
RUBBER LATEX
ABOUT COMPANY
Ngoc Chau Rubber is one of the private natural rubber manufacturers and exporters in Vietnam. They have a strong financial source, stable raw materials, modern production technology and a team of professional staff who are dedicated to their profession. On average, Ngoc Chau can supply customers with 20,000 tons of quality natural rubber.
PRODUCT
WHY CHOOSE US

PROFESSIONAL TEAM
We have a professional design team to give you the best solution.

POWERFUL FACTORY
We have advanced production equipment professional production line excellent QC team

ODM & OEM
We support OEM & ODM service, can better meet the customers.

QUALITY SERVICE
We provide not only good after service, but also best service affirmations to the customer.
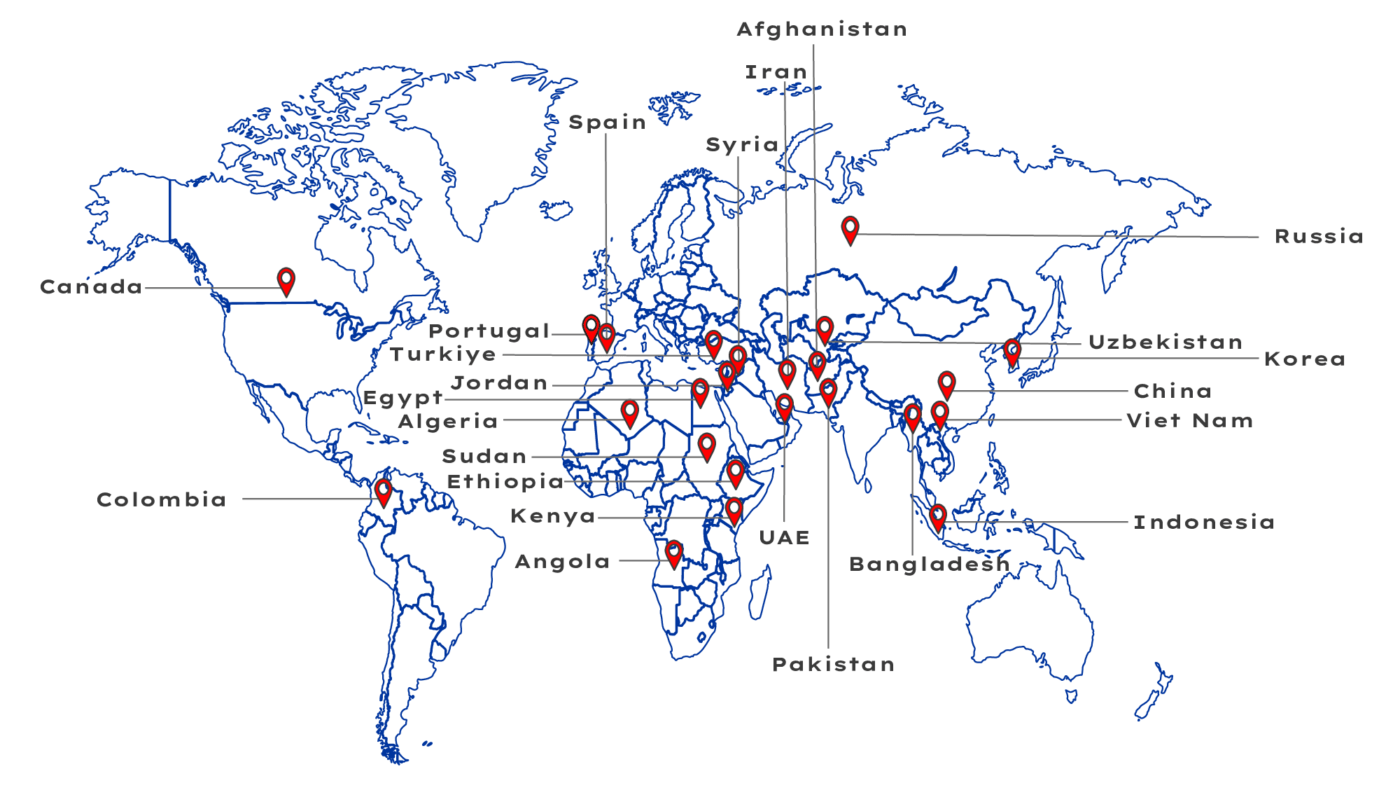
MARKET
CUSTOMER
Mr. Sarfaraz – Pakistan
“It is perfect! A great match. Exactly what we need. We still have enough for the lab trials we are doing. As part of our coating we are getting amazing performance”
Mr. Victor – Russia
The customer said: “When the loader unloaded. He said that the smell is like a good latex. Sweet and ammonia feels good.”
Mr. Benjamin – Canada
“The rubber arrived, and it is compatible! We are working to secure IP and manufacturer.”
Mr. Inkaya – Türkiye
“That looks perfect! Your service quality is very satisfied”
GOOGLE MAP








 Ms Evan
Ms Evan